
Overview
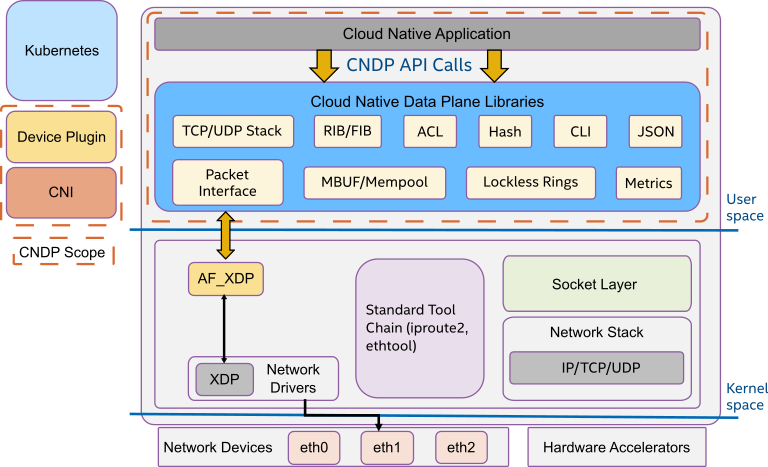
Cloud Native Data Plane (CNDP) is a collection of userspace libraries for accelerating packet processing for cloud applications. It aims to provide better performance than that of standard network socket interfaces using an I/O layer primarily built on AF_XDP, an interface that delivers packets directly to userspace, bypassing the kernel networking stack. CNDP provides a custom TCP/UDP stack, libraries for RIB, FIB, ACL, Hash, etc. It also provides JSON parsing and libraries to expose metrics and telemetry with examples to deploy services on Kubernetes.
Why CNDP?
Packet processing applications can be difficult to efficiently automate and orchestrate by a cloud native platform. This is especially true when deploying an application across different environments spanning private, hybrid, and public clouds. CNDP addresses this by providing a lightweight packet processing framework, designed and built for cloud native applications.
CNDP Consumers
-
Cloud Network Function (CNF) and Cloud Application developers: Those who create applications based on CNDP. CNDP hides the low-level I/O, allowing the developer to focus on their application.
-
CNF and Cloud Application consumers: Those who consume the applications developed by the CNF developer. CNDP showcases deployment models for their applications using Kubernetes.
CNDP Characteristics
CNDP follows a set of principles:
-
Functionality: Provide a framework for cloud native developers that offers full control of their application.
-
Usability: Simplify cloud native application development to enable the developer to create applications by providing APIs that abstract the complexities of the underlying system while still taking advantage of acceleration features when available.
-
Interoperability: The CNDP framework is built primarily on top of AF_XDP. Other interfaces, such as memif, are also supported, however building on AF_XDP ensures it is possible to move an application across environments wherever AF_XDP is supported.
-
Portability/stability: CNDP provides ABI stability and a common API to access network interfaces.
-
Performance: Take advantage of platform technologies to accelerate packet processing or fall-back to software when acceleration is unavailable.
-
Observability: Provide observability into the performance and operation of the application.
-
Security: Security for deployment in a cloud environment is critical.